Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
Put Data into a UserForm
How to take data from Excel and put it into a UserForm. This is useful when you use a form to display/edit data that is stored within worksheets.
This includes these controls: labels, text inputs (TextBox), list boxes (ListBox), drop-down menus (ComboBox), checkboxes (CheckBox), and option buttons (OptionButton).
Note: this tutorial assumes that you have already filled applicable controls with default values when the form was initialized; as in, there are already values in the ListBox and ComboBox on the form. If that is not the case, view these tutorials: Add Values to a ListBox Add Values to a ComboBox.
Sections:
How to Get a Value from the Worksheet
Where to Put the Code
The code for each control should go into whatever event causes the control to be filled with a value.
If a user clicks a button and then values should be put into the form, then the code should go into the Click event for that button.
Here is what is might look like in the code window for a form:
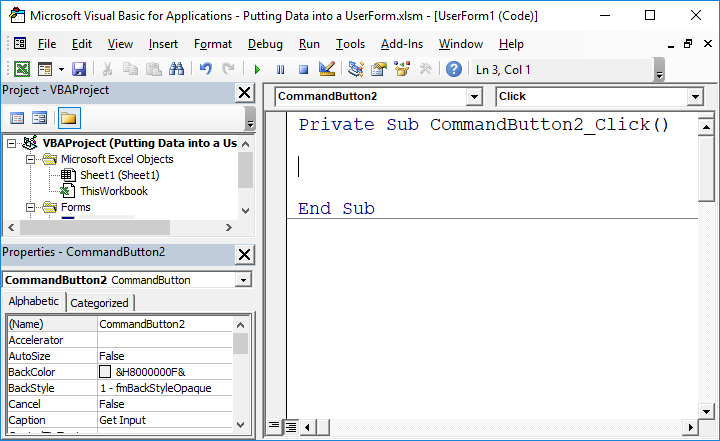
If you would like to learn more about events and how to make code run when a user does something, such as clicking a button, view our tutorial on UserForm Control Events.
How to Get a Value from the Worksheet
The first thing to do is to get data into the form so that we can do something with it. Here, I'll show you a very simple way to get any value from any cell in Excel and to store that value into a variable so that we can easily insert it into a control in the UserForm.
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").ValueSheet1 is the name of the worksheet that contains the value you want to get.
A2 is the cell that contains the value that you want to get.
Now, let's put this value into a variable so we can use it.
LabelValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").ValueLabelValue is now the variable that will hold the value of cell A2 from Sheet1. To reference this value lower in the code, we just use LabelValue instead of writing out all of the code.
Label
Label1.Caption = LabelValueLabel1 is the name of the label that we want to put text into.
LabelValue is the variable to which we assigned our text from the worksheet.
Useful Example
'Get values from the worksheet
LabelValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").Value
'Put Value into the label
Label1.Caption = LabelValue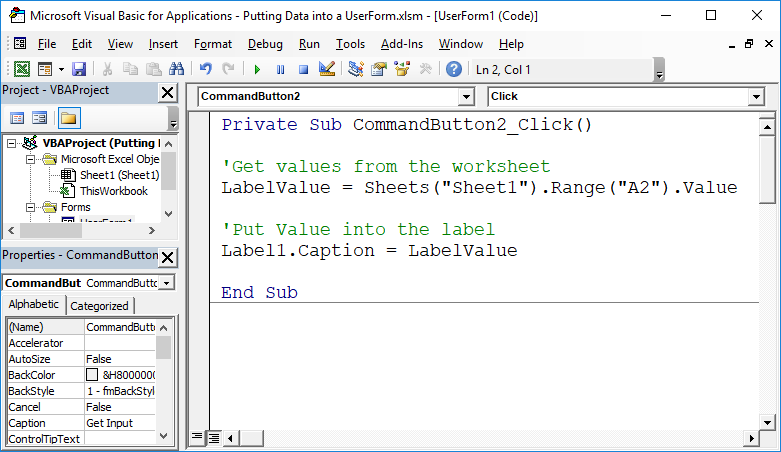
TextBox
TextBox1.Text = TextBoxValueTextBox1 is the name of the TextBox.
TextBoxValue is the name of the variable that holds the value from the worksheet that we want to put into the TextBox.
Useful Example
'Get values from the worksheet
TextBoxValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").Value
'Put Value into the textbox
TextBox1.Text = TextBoxValue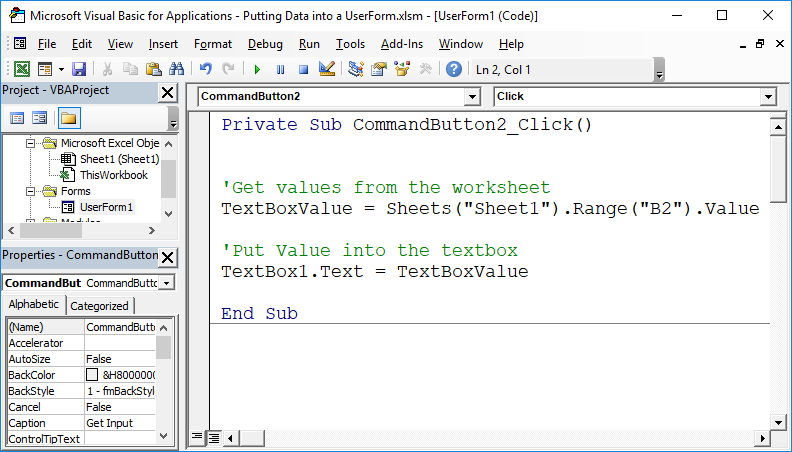
ListBox
To select an item in a ListBox, we have to loop through the items in the ListBox to see if it exsits and then, if we find it, use the index number of that item to select it; we can't simply use the name of the item to select it.
'Loop through the items in the ListBox
For i = 0 To ListBox1.ListCount - 1
'Check if the value from the worksheet is in the ListBox
If ListBox1.List(i) = ListBoxValue Then
'If here, then we found the item, so select it.
ListBox1.Selected(i) = True
'Since we found the item and selected it, we can exit the loop.
Exit For
End If
Next iListBox1 is the name of the ListBox.
ListBoxValue is the variable that contains the value from the spreadsheet.
This code may look confusing, but you only need to change the two items above, that are in bold, to get it to work for your example. The rest of the code simply loops through all of the items in the ListBox to check if the value from the spreadsheet exists in the list and it then selects it if a match is found. To do this, we use a For loop and an IF statement.
Useful Example
'Get value from the worksheet
ListBoxValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("C2").Value
'Check if the worksheet value exists and select it.
'Loop through the items in the ListBox
For i = 0 To ListBox1.ListCount - 1
'Check if the value from the worksheet is in the ListBox
If ListBox1.List(i) = ListBoxValue Then
'If here, then we found the item, so select it.
ListBox1.Selected(i) = True
'Since we found the item and selected it, we can exit the loop.
Exit For
End If
Next i
End Sub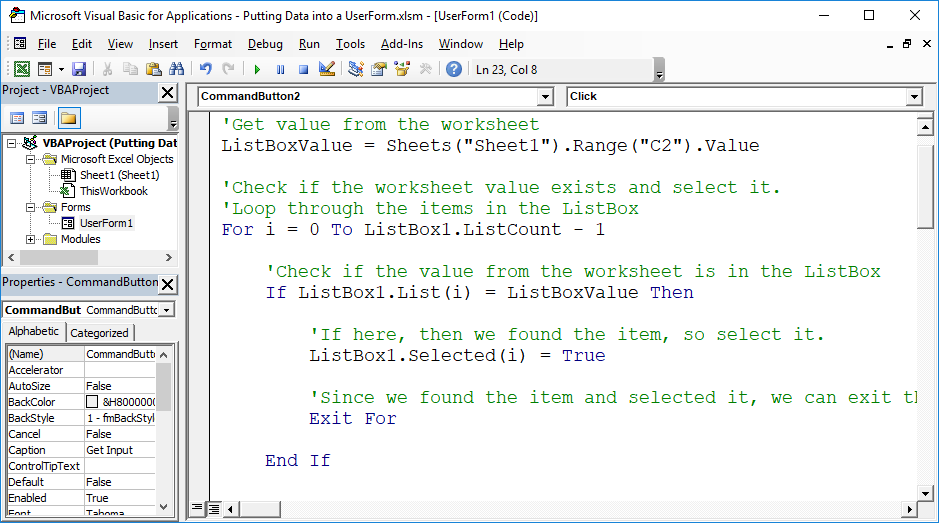
ComboBox
This is similar to what is done in the ListBox example above, but there is a small difference, explained below.
To select an item in a ComboBox, we have to loop through the items in the ComboBox to see if it exsits and then, if we find it, use the index number of that item to select it; we can't simply use the name of the item to select it.
'Loop through the items in the ComboBox
For i = 0 To ComboBox1.ListCount - 1
'Check if the value from the worksheet is in the ComboBox
If ComboBox1.List(i) = ComboBoxValue Then
'If here, then we found the item, so select it.
ComboBox1.ListIndex = i
'Since we found the item and selected it, we can exit the loop.
Exit For
End If
Next iComboBox1 is the name of the ComboBox.
ComboBoxValue is the variable that contains the value from the spreadsheet.
This code may look confusing, but you only need to change the two items above, that are in bold, to get it to work for your example. The rest of the code simply loops through all of the items in the ComboBox to check if the value from the spreadsheet exists in the list and it then selects it if a match is found. To do this, we use a For loop and an IF statement.
This is different from the ListBox example because, here, we use the ListIndex property to select the item.
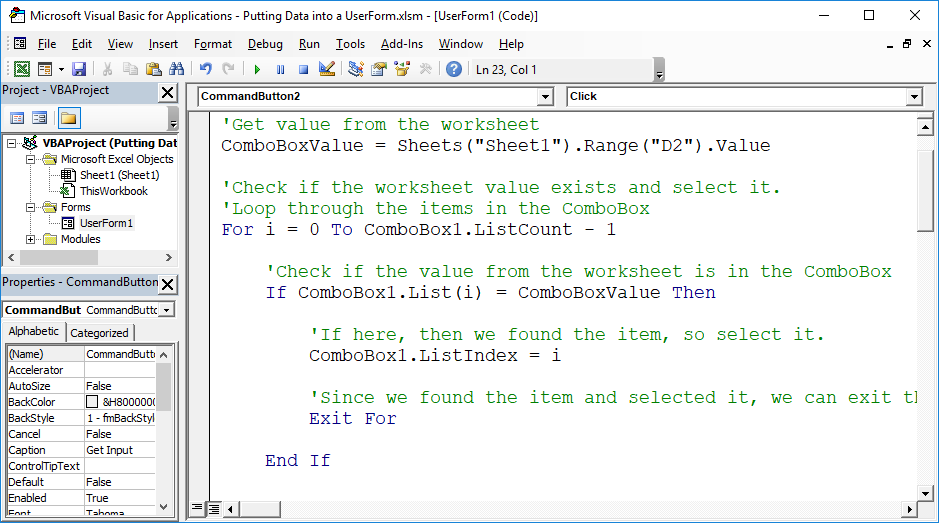
Useful Example
'Get value from the worksheet
ComboBoxValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("D2").Value
'Check if the worksheet value exists and select it.
'Loop through the items in the ComboBox
For i = 0 To ComboBox1.ListCount - 1
'Check if the value from the worksheet is in the ComboBox
If ComboBox1.List(i) = ComboBoxValue Then
'If here, then we found the item, so select it.
ComboBox1.ListIndex = i
'Since we found the item and selected it, we can exit the loop.
Exit For
End If
Next i
CheckBox
CheckBox1.Value = CheckBoxValueCheckBox1 is the name of the checkbox.
CheckBoxValue is the value from the worksheet. This must be either True or False.
Useful Example
'Get value from the worksheet
CheckBoxValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("E2").Value
'Make sure the value is True or False or default to False
If CheckBoxValue <> "True" Then
CheckBoxValue = "False"
End If
'Set the CheckBox Value
CheckBox1.Value = CheckBoxValue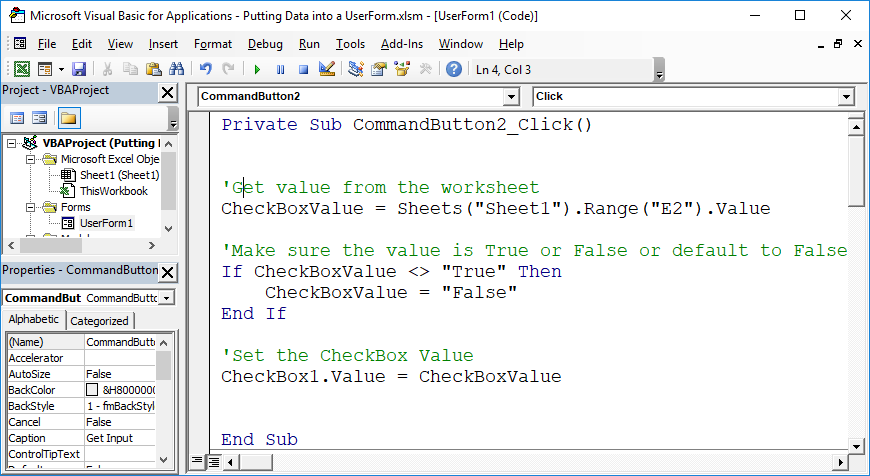
The first part gets the value from the spreadsheet - remember that the value must be either True or False. Or, if you want, you can allow the user to enter other values and then just convert them to True or False within the code.
The second section makes sure that the value is True or it sets it to a default value of False.
The third section updates the checkbox in the form.
OptionButton
This requires a loop to go through the available option buttons and then match the value from the worksheet with the correct OptionButton.
'Loop through the controls in the form.
For Each FormControl In Me.Controls
'Check only OptionButtons.
If TypeName(FormControl) = "OptionButton" Then
' Check the value of the OptionButton.
If FormControl.Caption = OptionButtonValue Then
'Match was found, so select that option button.
FormControl.Value = True
'Exit the For loop.
Exit For
End If
End If
Next
OptionButtonValue is the value from the worksheet.
In this example, you don't need to know the name of the OptionButton because the code loops through all of them in order to select the correct one.
This code uses the caption of the OptionButton to match with the value in the worksheet. This means that if the worksheet value was "Male", the code looks for the OptionButton that has the visible caption "Male" and, if it finds it, it selects it.
There are other ways to do this, such as specifically referencing the name of the OptionButton that you want to select, but the method illustrated above is often easier to use.
Useful Example
'Get value from the worksheet
OptionButtonValue = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("F2").Value
'Loop through the controls in the form.
For Each FormControl In Me.Controls
'Check only OptionButtons.
If TypeName(FormControl) = "OptionButton" Then
' Check the value of the OptionButton.
If FormControl.Caption = OptionButtonValue Then
'Match was found, so select that option button.
FormControl.Value = True
'Exit the For loop.
Exit For
End If
End If
Next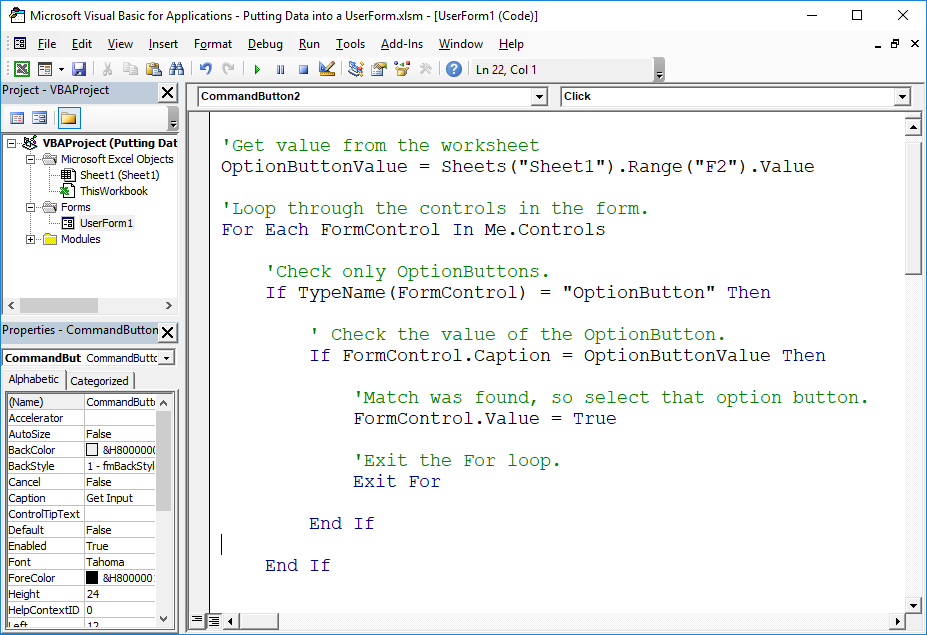
Notes
Putting data into a UserForm can get complicated, especially if you have large forms with many sets of controls; this is especially true once you account for what the user may enter into the spreadsheet from which the form data will be taken.
Download the sample file for this tutorial to see all of the code and examples from above. (The data that is pulled into the form is located in row 2 of the downloadable spreadsheet.)



